

Discover more from Agent131711’s Substack
Part 2🦕The Dinosaur HOAX: PSYOPS & SCHEMES: Faking Footprints and Worldwide Collusion
PART 2: A hilarious "history" lesson: the entire world began finding "dinosaur fragments" at the same time.
Let’s recap what we learned in Part 1:
In the late 1700s, a member of The Royal Society was able to determine the existence of prehistoric creatures due to his “uncanny ability” to identify species from only a couple random bones.
Two rich AF dudes (a Quaker Oatmeal heir and dude whose uncle had a city named after him) discovered damn-near all of the dinosaurs of that time. Yep, two guys found not one, not two, not three bones, but discovered over a thousand extinct species, including hundreds of dinosaurs.
The oatmeal bro then wrote 1,400 scientific papers, which became fact
And the other dudes uncle (who had the city named after him) created archeology programs at colleges and opened libraries and museums because when you control the content, you control history.
The only people to find dinosaur skeletons are governments, fossil hunters working for museums and the elites.
None of us can find dinosaur bones and we aren’t even allowed to actually see them in museums
The dinosaur bones in the museums are also fake; made from chicken bones, frog bones, horse bones, dog bones, plaster, plastic and more… to protect us from radiation… and also they’re just too valuable, too rare and too heavy for us to be able to look at…
Even the experts are barred from seeing the real bones (and the one recent time an expert could see them, he ran them through a CAT scan and discovered they were all fake)
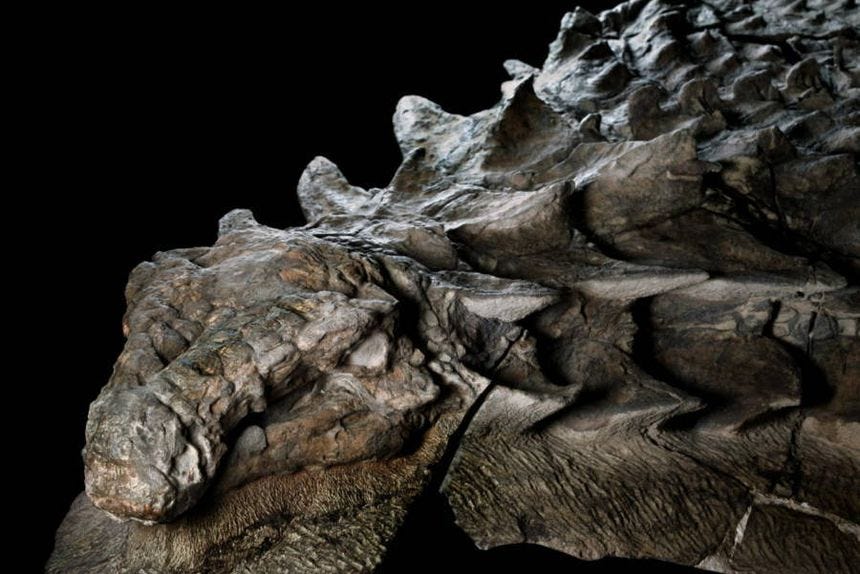
Also, in Part 1, we learned that, in December 2023, a first-ever-most-complete-skull was found, but when I dug deeper, the discovery appears super nefarious because the land is protected by the United Nations and the dude who made the discovery is a museum owner who happens to have nearly a dozen new-species discoveries, including seven dinosaurs named after him.
And here we are. Today we are going to continue on with The Dinosaur Hoax; slowly dismantling a historic prehistoric lie.
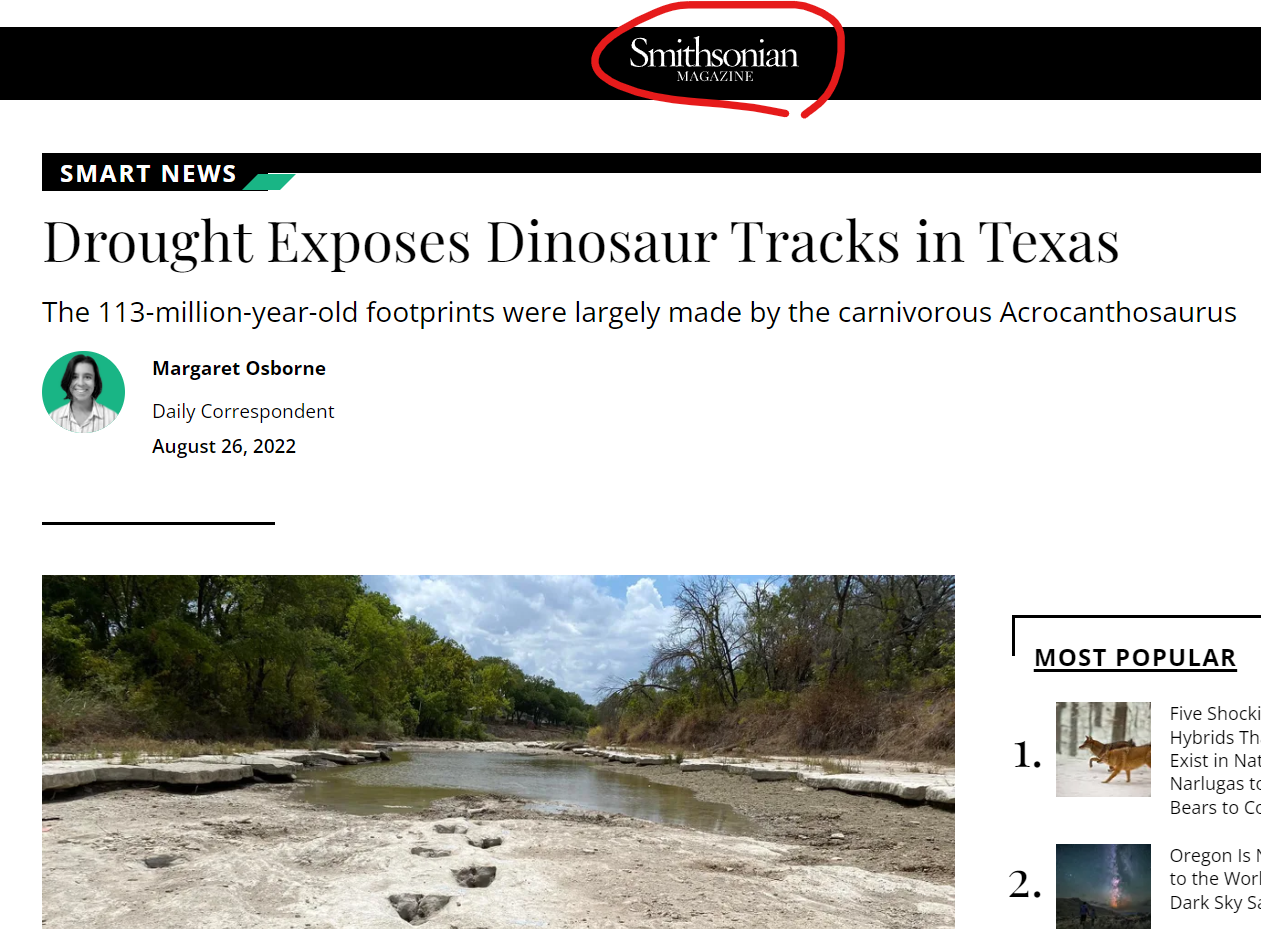
Let’s start by by looking at The Footprints, which are historical evidence in Texas, proving that dinosaurs once roamed freely in the state. Check out 1-minute clip I snipped from a real documentary (if I recall correctly, this aired on The History Channel, BBC or National Geographic in the 1990s):
Now lets look at the truth about the Texas footprints… (4 minute video. Volume is a little low so you might have to turn it up. Trust me, it is totally worth your time)
Ok, so the footprints that are still promoted as being real, are admittedly fake, according to the guy who put them there.
Should we bring out the red flags? Yes we should…
When I was writing Part 1, I noticed that nobody had taken the time to go through the discoveries of the most popular dinosaurs, like T-Rex, Triceratops, Stegosaurus and Brontosaurus, so I figured we can do that together today. Little did I know, I was in for one hell of a rabbit hole… this is legitimately an incredible history lesson that will stick with you for the rest of your life.
THE DINOSAUR DISCOVERY RABBIT HOLE
Ankylosaurus
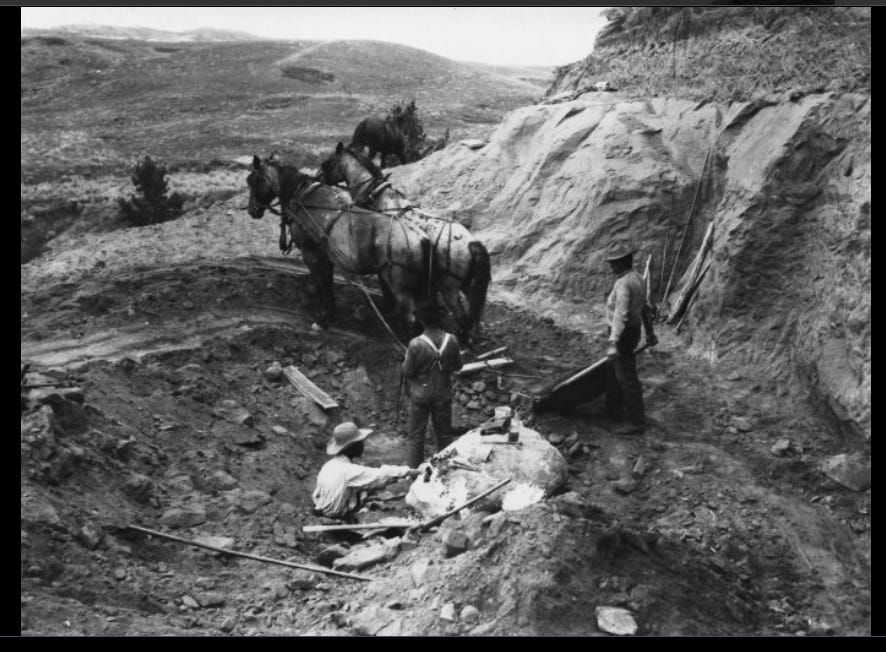
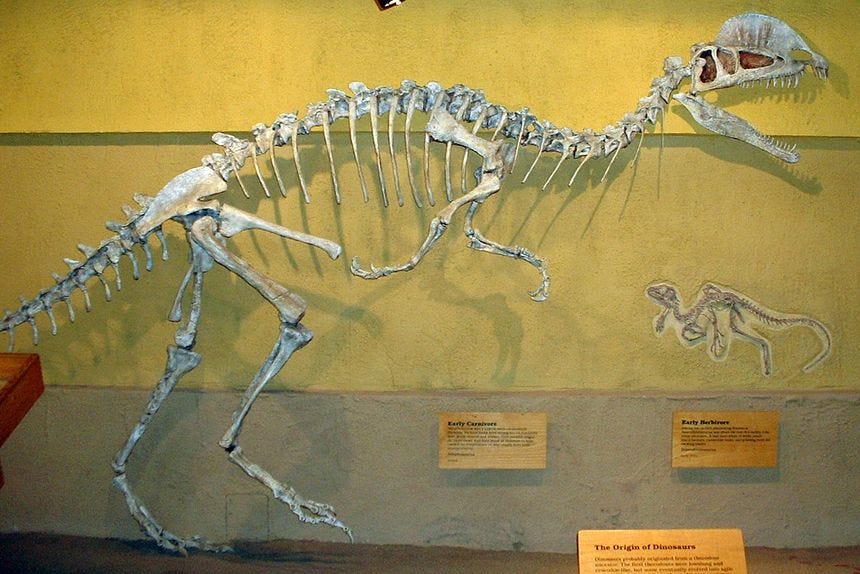
The Ankylosaurus might be my favorite story of all; Do you remember Othniel Charles Marsh from the first part of this series? He was one of the two guys who discovered basically all of the dinosaurs; he’s the bro whose uncle owned the museums, libraries, established paleontology programs at colleges, yada-yada. Well, in 1892, Mr. Marsh was able to determine the “Ankylosaur Palaeoscincus “ based on a single tooth. However, the first Ankylosaurus bones were not found until 1906, at the Hell Creek Formation in Montana, and you are going to love this tale:
Barnum Brown led the fossil hunting trip.
“Who is Barnum Brown?”, you ask.
I reply, “Mr. Brown has quite an interesting story. During World War I and World War II, he worked as an intelligence asset.”
With a look of confusion you say, “For the military?…”.
I chuckle and respond, “No Sweetheart. He was a corporate spy for oil companies… or, should I say, he was a corporate spy for the Rockefellers Fossil Fuel industry…”. I then add, “This spy dude was nicknamed Mr. Bones, because, other than working in espionage, he was also an American paleontologist. Not only did he discover the Ankylosaurus bones, but he also discovered the first documented remains of Tyrannosaurus, which skyrocketed him to fame. He instantly became the one of most famous fossil hunters in history. Pretty amazing, eh?”.
Speaking of T-Rex…
Tyrannosaurus
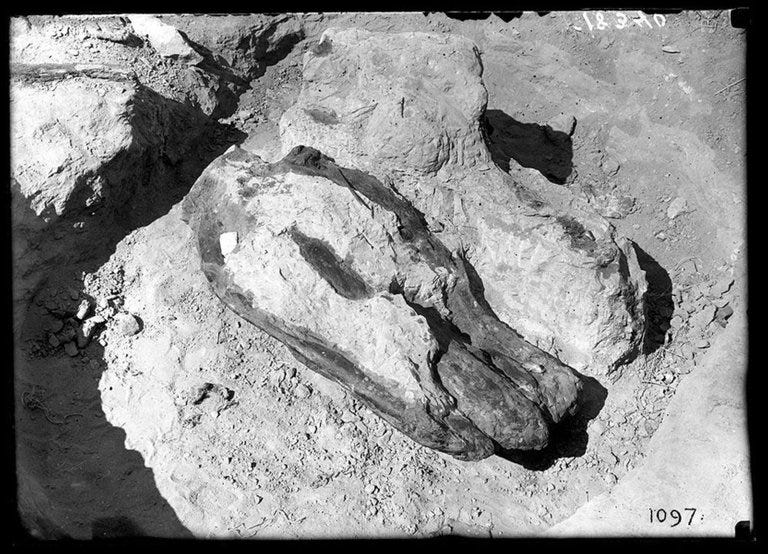
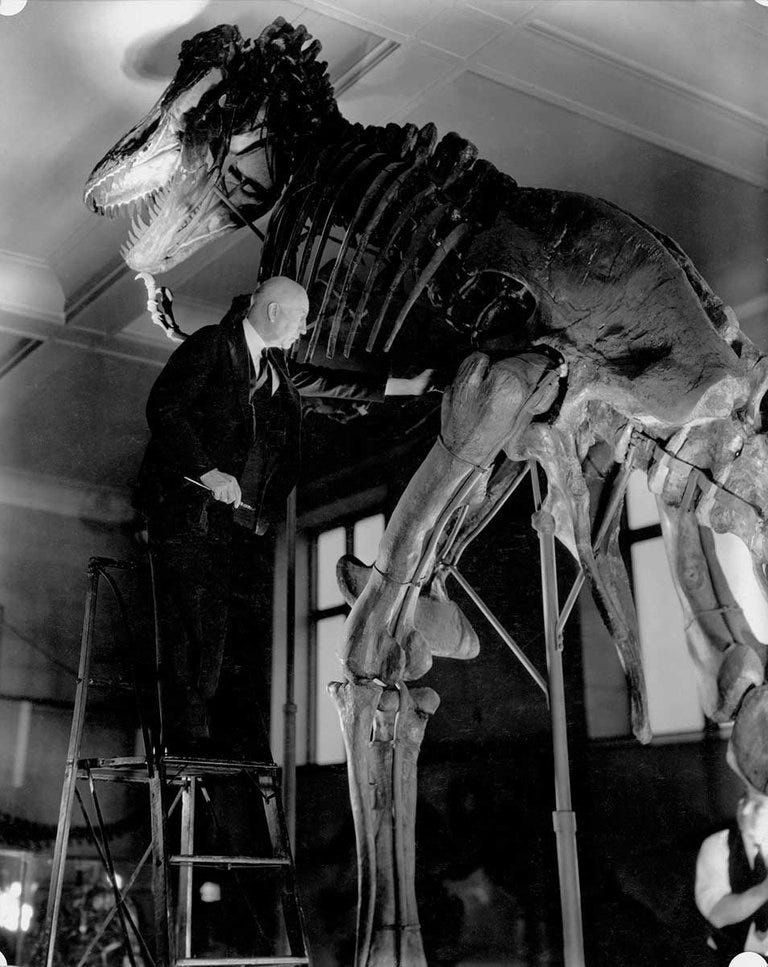
The plot thickens… not only was it discovered by the spy, Barnum Brown, but guess where he worked at the time of the discovery? Brown was the assistant curator of the American Museum of Natural History. The story claims that he found the first-ever partial skeleton of a T-Rex in 1900, and luck was on his side because he discovered another in 1902! The president of the American Museum of Natural History (his employer), checked out the bones and “confirmed them”, then named it T-Rex. Here is all of the evidence you need to know this is real:
And here it is, put together, in the museum, ready to draw crowds:
History writes, “In 1941, the T. Rex type specimen was sold to the Carnegie Museum of Natural History in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, for $7,000”. Yes, the “t-Rex type specimen” .
Next thing ya know, 42 T-Rex skeletons were found, just in the Western area of North America. Then, a couple decades later, in the 1990s, the findings skyrocketed. Just in this single decade, over 84 T-Rex skeletons were discovered. In the summer of 2000, one dude found five on his own, in one area.
Spinosaurus
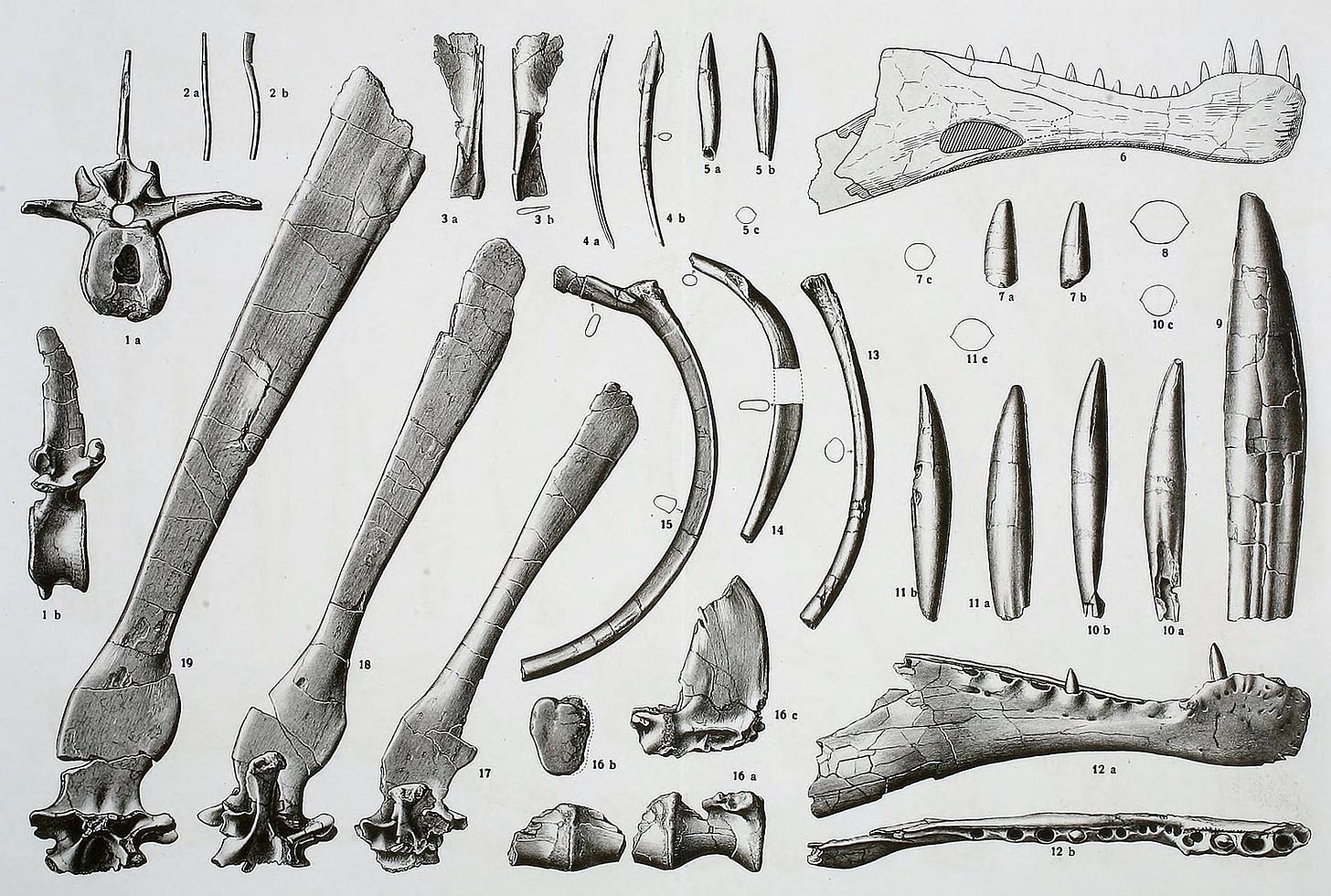
History claims that, in 1912, Richard Markgraf, Austrian paleontologist, discovered “a partial skeleton” of an unknown dinosaur while on an expedition in Western Egypt. Here’s a drawing of Richards findings:
A German paleontologist was able to look at the art and conclude this undoubtedly was a new species. He then chose a name and published an article stating these bones all belong to Spinosaurus aegyptiacus. But, the story doesn’t end there…
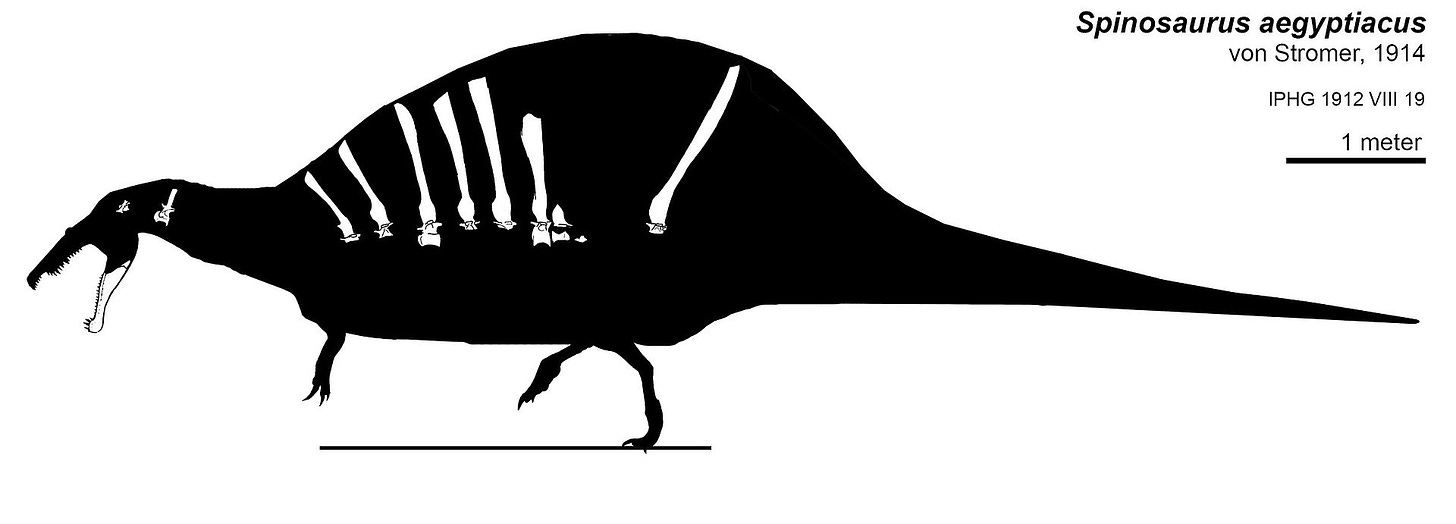
During World War II, the museum was bombed, which destroyed all of the evidence of the Spinosaurus! I know, you’re devistated, right? But, you can turn that frown upside-down! The great news is, what miraculously survived the bombing was the drawings and “detailed descriptions” that had been written by scientists and paleontologists!:
So, they were able to use the art and notes to recreate all of the bone evidence that had been lost! PRAISE JESUS! These recreations allow us to see what was forever-lost in the attack on the museum!:
Sadly, this wasn’t the only dinosaur to be destroyed. Meet the:
Hadrosaurus
This dinosaur was discovered in 1838, by a guy named John Hopkins. This information would later appear in Johns Hopkins magazine (Johns Hopkins University). History claims John Hopkins thought his discovery was junk and gave away the skeleton… where it magically ended up on display at the Academy of Natural Sciences:
Guess who built the fossil statue? None other than the Quaker Oatmeal heir who discovered half the dinosaurs, Edward Drinker Cope!
The media reports that this single exhibit greatly increased awareness of dinosaurs. They wrote, “About 30,000 people a year normally visited the Academy. But during the first year after Hadrosaurus went on display, the number more than doubled to 66,000. The following year, it went to 100,000. Finally, the masses, jostling to see a real dinosaur, literally drove the Academy out of its building”. The Academy of Sciences quickly secured a substantially larger building to showcase more discoveries and, just like that, financially lucrative Dinosaur Museums and were officially born as a mainstream industry.
But in 1871, horror struck. A gang of street thugs completely destroyed the priceless Hadrosaurus. To make matters worse, after the evil gang ruined the dinosaur, they threw the pieces into a lake, and there was no way to ever recover it! History was forever destroyed that fateful night. But, just when you think all hope is lost…
In the late 1870s, another copy of Hadrosaurus was acquired by the Smithsonian Institution, which meant the world-famous skeleton was back on display, and more dinosaur awareness could be raised!
Brontosaurus PSYOP
Here’s another great bedtime fairytale history-tale to tell your children:
Guess who found the Brontosaurus? Of course it was Marsh, the I-have-a-rich-uncle-who-owns-museums dude! However, the skeleton he discovered is still one of the most incomplete skeletons ever, but problems like this are easily handled by Science… and the United States Postal Service!
How Science found the missing pieces: To cut to the chase, Marsh used bones from his other discoveries. But it wasn’t just a couple bones that were substituted for the missing skeleton parts… he even grabbed a skull from a different beast, threw it on the Brontosaurus and Voilà! The dino was complete! The Carnegie Museum of Natural History displayed the hack-job-history, the media gobbled it up, and Brontosaurus came-to-be.
In the 1970’s it was finally admitted that the skeleton was erroneous, but that didn’t stop the United States Postal Service (USPS), a government agency, from releasing dinosaur postage stamps featuring the imaginary creation… then a huge PSYOP was ran on the American Public…
So, USPS released the stamps, and the media immediately began reporting that the public was “outraged”. The news reported people were really upset at the Post Office for "fostering scientific illiteracy" … but, the PSYOP part of this event was when the media stated the outrage was over incorrectly calling it a Brontosaurus. The news claimed the people demanded a stamp recall so that the stamps could be reprinted, with the correct name of the species, which is actually Apatosaurus. …see the Psychological Operation here? They are reinforcing that this dinosaur nonsense is 100% real and that the only inaccurate thing is the name of that species.
Triceratops
So, the story with the Triceratops is, in 1887, “a pair of brow horns attached to a skull roof” were found by George Lyman, a fossil collector who was working for the Geological Survey of Canada. Here’s his drawing of his discovery:
Georgie-boy sent his find to Mr. Marsh, who somehow was able to date the alleged bones to the Pliocene Era (3 to 5 million years ago) and somehow identify it as a Triceratops. The following year, Marsh somehow discovered even more horned dinosaur bones, followed by a complete skull! WOW!
Between 1889 and 1891, 31 more skulls were discovered. Yep, in under 24 months, over 31 additional triceratops skulls were found… somehow…
Oh, and I should mention, by 2014, over 50 skulls had been found, but they were all a little bit different from each other, this inconsistency was chalked up to the Triceratops evolving and “new subspecies”.
Velociraptor
The American Museum of Natural History took an expedition to the Gobi Desert. Here a crushed skull was located. Back at the museum, they already had a claw that was located in the same desert, therefore, it was concluded that the claw must belong to the same animal as the skull, therefore, it was a new, extinct species discovery.
As time progressed and desert digging continued, many non-matching skulls were unearthed, which were all determined to be unique subspecies of Velociraptor:
Yes, I agree with you, they sure do look a hell of a lot like alligator skulls…
But how dare you imply a museum would ever lie! They would never even consider such a thing! You owe the museum and their crocodile skull an apology!
Stegosaurus
These bone fragments were found by, guess who? Marsh! In Wyoming in 1887. Clearly this is a Stegosaurus because there is nothing else these scraps could possibly be!:
These incredible findings fueled museums to go balls-to-the-wall with expeditions. It was no longer just the American Museum of Natural History finding extinct species bones, now the Carnegie Museum of Natural History, and the Field Museum of Natural History were sending crews all over the nation, which were bringing back literal loads of dinosaur bones. These rare discoveries made headlines and drove visitors to the museums, thus enriching everyone involved in the discoveries, thus leading to more and more findings, more and more new species and subspecies, thus leading to more and more museum patrons. See how that works?
Pterodactyl
This story might be your fav:
The most famous flying dinosaur started as an engraving in copper… yes, you did read that correctly… but the engraving was based on bones unearthed in Germany, but we don’t know when they were unearthed, and for unknown reasons, this amazing discovery was never logged into the “collection catalog”, which was where all historic finds were recorded. Because of this, nobody knows much about it, but…
… thankfully, our buddy, Georges Cuvier, The Royal Society dude, was there to determine what these bones were! Do you remember this bro from Part 1? If not, here’s a quick, refresher because it is the foundation for the entire concept of The Theory of Evolution dinosaurs: (1 minute 29-second video)
So, at some point in time, copper was engraved based on bones. A drawing of the copper engraving was sent to Royal-Society-George, who determined, from the art, that this was a reptile. Georgie then named the reptile drawing discovery, Petro-Dactyle, and boom! It was written, it was repeated, and it became fact.
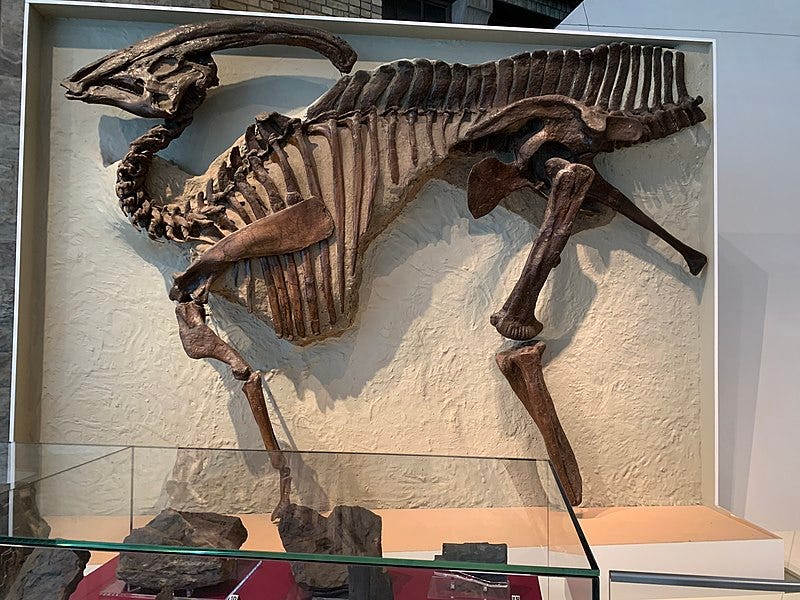
Parasaurolophus
Did you also read it as, “Para-saur-lop-a-what?”
Do you remember the “Dinosaur Dig Parks” from Part 1? (9 second video)
We are told this very-first-ever Parasaurlopawhat Parasaurolophus was discovered by fossil hunters from the University of Toronto in the Alberta, Canada Dinosaur Park:
Get this: when the University discovered this nonsense these bones, paleontologist William Parks named the specimen “P. walkeri” in honor of Sir Byron Edmund Walker, the chairman of the Board of Trustees of the Royal Ontario Museum. And let me tell you, Sir Byron has a story of his own:
Not only was he an ultra-elite who was president of the Canadian Bank of Commerce, but he also established Canadian banking laws and regulations, in addition to programs at universities. He even founded the Royal Ontario Museum, at which he was chairman of the Board of Trustees. He is a “Sir” because he was knighted by King George V. ...and now he had a dinosaur named after him. His Bucket List was complete.
Other than the Universities Fossil Hunters, very few of this extinct species bones have been discovered, anywhere, ever. The “best skull ever discovered” is this:
… which is amusing, because the original skull that was found by the university looks a hell of a lot better than the “best-skull-ever”, does it not?:
My bullshit detector goes beep … beep … beep …
Diplodocus
To date, no skull has ever been found that can confidently be said to belong to Diplodocus, but who needs a skull when you have Science?
The first Diplodocus discovery was made at a dinosaur dig quarry by a huge Evolutionist, Samuel Wendell Williston. Guess who paid for this expedition? None other than Marsh, who was overseeing his rich uncle’s paleontology program at Yale University.
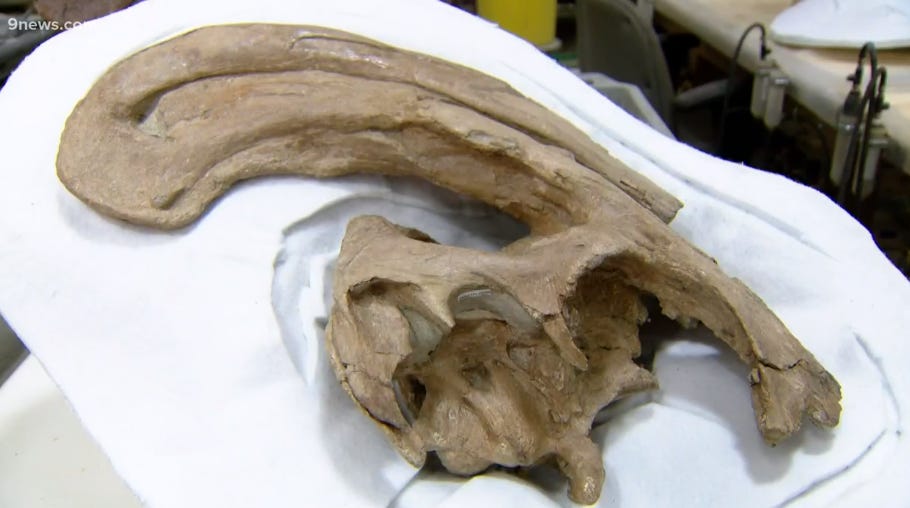
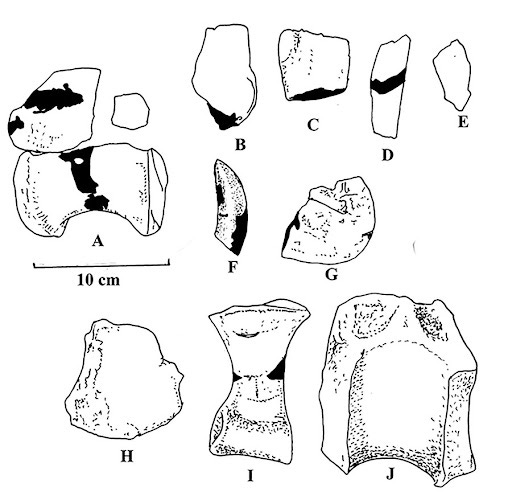
Samuel’s Diplodocus discovery (#YPM VP 1920) was admittedly “very incomplete”, consisting only a handful of random bones. Here’s what we get to see:
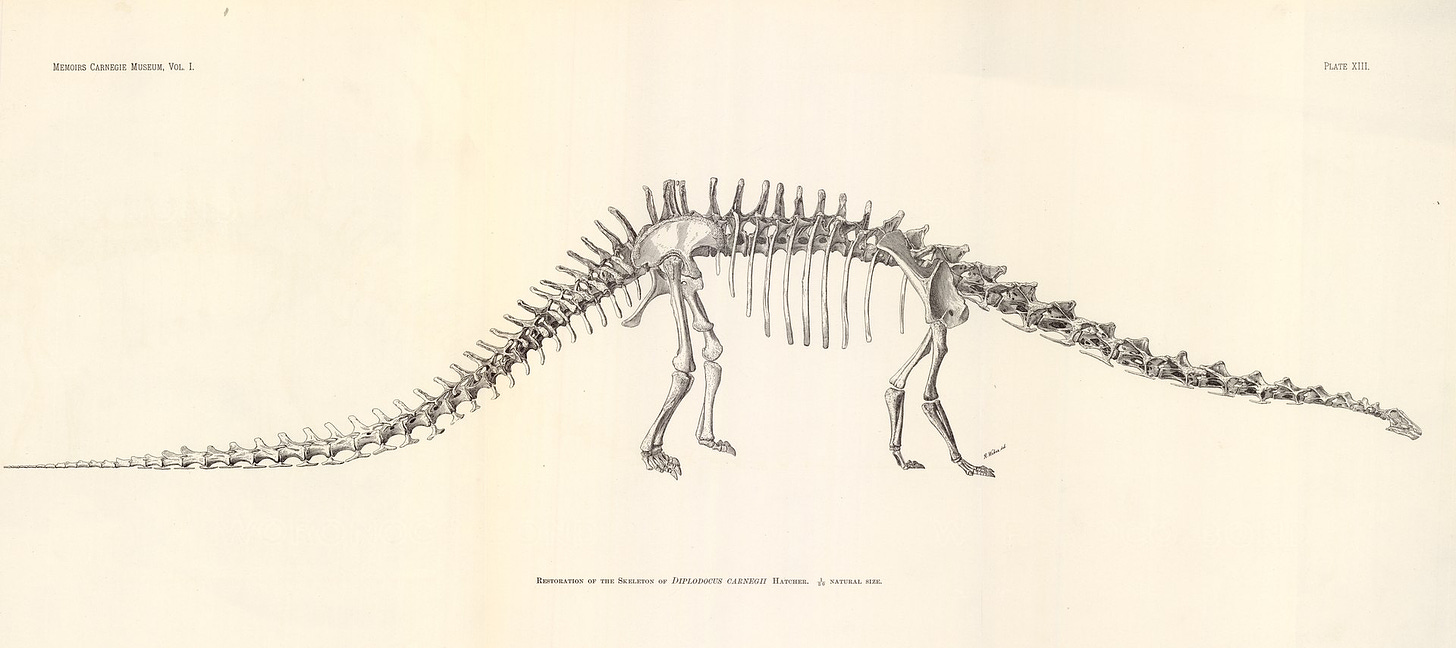
Thankfully, they were able to use those bones and figure out the dinosaur looked like this:
The bones were sent to Marsh’s uncle’s Yale Peabody Museum where Marsh named this new species Diplodocus longus.
The general public was excited to see the newest dinosaur.
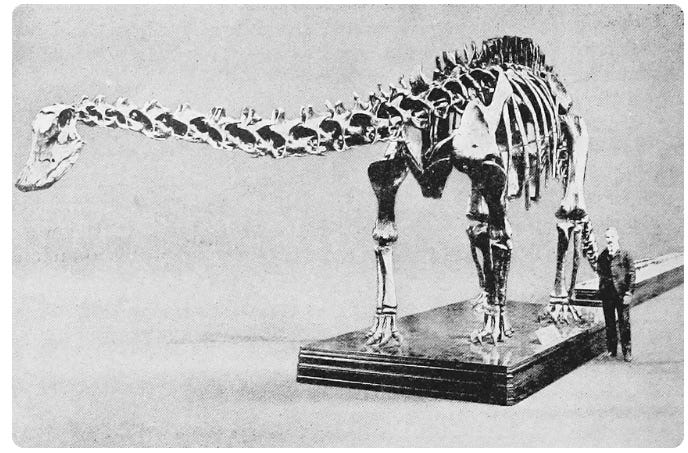
Then, Diplodocus began appearing in museums all over the world:
Admittedly, all of these are casts (replicas) of the original, because nobody else had found the bones, but the museums all wanted to make sure the public could see it, so they just made copies. Surprisingly, Carnegie (of all people) admitted his was a replica, whereas others did not:
Brachiosaurus
Here’s another gem of a story. A paleontologist working for the Field Columbian Museum (now known as the Field Museum of Natural History) made this incredible discovery after the president of the Western Colorado Academy of Science told him to go dig in a specific area. (Because that’s not suspicious or anything)
The Academy of Science president told the fossil hunter that bone discoveries had been made in a specific area for decades. Sure enough, during the first days of the expedition, historic discoveries were made.
The findings were brought back to the scientists and paleontologists:
And eventually, the Brachiosaurus was officially born, in museums. YAY!:
Pachycephalosaurus
Just like with the Pterodactyl, we don’t know when exactly the bone fragment was found, so we just say, “As early as the 1850s”, because Donald Baird, “an influential and innovative vertebrate paleontologist”, said so. One of these are supposed to be a replica of “the fragment”, which was determined to be part of the skull of the new species of dinosaur:
In 1943, Barnum Brown (the oil-industry spy dude who discovered the T-Rex and the Ankylosaurus and worked for the museum) was able to determine there was a new species of dinosaur which he called “Pachycephalosaurus” , based on Science.
In the 1960s, this “nearly complete skull” was located by paleontologists:
Now here’s where the story get’s even more interesting. Do you remember how Marsh named the Ankylosaurus based on a single tooth? Well, in 1990, Walter P. Coombs (a dinosaur expert) realized that single tooth was actually from a Pachycephalosaurus, not an Ankylosaurus (Lol).
Dilophosaurus
Yet another fantastical story. This is def in my top 5 favs:
What had happened was, in 1942, the University of California Museum of Paleontology was in Arizona, digging for fossils. Somehow the local Indian tribe heard they were digging and came to tell them that the Indians had found three of the same dinosaurs, embedded into shale, in a triangle pattern. The Indians took the paleontologists to their reservation to see the dinos. The paleontologists confirmed these were full skeletons but, because they were on Indian territory, the bones could not leave the property and no photos were taken. The good news is, the paleontologists now knew what this extinct animal looked like.
Only a few years later, this “most complete specimen” officially became a new species. Look how complete this is!:
It was officialy given a name in 1954, the Dilophosaurus.
Eventually, the Indians would let the University of Texas take this single Dilophosaurus “right hind leg” and store it in trust, in the schools Paleontology Collection. How nice of them!
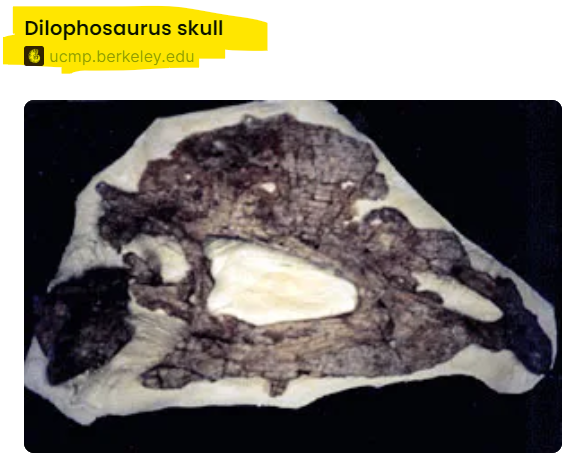
It would take Science until the 1970s to determine that this dinosaur had a crest on its head. From what I understand, it was this “skull” that lead to the revelation:
Surprisingly, there is not much more information on the Dilophosaurus. All we know is that this is currently on display at the Royal Ontario Museum in Toronto, Canada:
And there's this “reconstructed skeleton”, on display at the Academy of Natural Sciences:
NEXT: READ PART 3: THE INNER WORKINGS OF A SHAM
But first:
NEXT READ
If you haven’t read PART 1:
OR CHECK OUT:
SOURCES, NOTES & OTHER SH*T
This is my note pad that I use while I write. I leave it all in here for anyone who feels like looking at it. Sometimes I cut content out of the body of the article, and instead of deleting it forever, I move it down here:
Brontasaurus hoax
https://www.infoplease.com/great-brontosaurus-hoax-1
_____
The first Ankylosaurus bones were found in 1906 at the Hell Creek Formation in Montana, USA. Barnum Brown led the fossil hunting trip
https://www.nhm.ac.uk/discover/dino-directory/ankylosaurus.html
Barnum Brown (February 12, 1873 – February 5, 1963), commonly referred to as Mr. Bones, was an American paleontologist. Named after the circus showman P. T. Barnum, he discovered the first documented remains of Tyrannosaurus during a career that made him one of the most famous fossil hunters working from the late Victorian era into the early 20th century.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barnum_Brown
***
During World War I and World War II, he worked as an "intelligence asset". During his many trips abroad, he was not above picking up spare cash acting as a corporate spy for oil companies.
________
Triceratops - Othniel Charles Marsh
The first named fossil specimen now attributed to Triceratops is a pair of brow horns attached to a skull roof that were found by George Lyman Cannon near Denver, Colorado, in the spring of 1887.[3] This specimen was sent to Othniel Charles Marsh, who believed that the formation from which it came from dated from the Pliocene and that the bones belonged to a particularly large and unusual bison, which he named Bison alticornis.[3][4] He realized that there were horned dinosaurs by the next year, which saw his publication of the genus Ceratops from fragmentary remains,[5] but he still believed B. alticornis to be a Pliocene mammal. It took a third and much more complete skull to fully change his mind.
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triceratops
31 SKULLS!
After Triceratops was described, between 1889 and 1891, Hatcher collected another thirty-one of its skulls with great effort.
_____
Velociraptor
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Velociraptor
During an American Museum of Natural History expedition to the Flaming Cliffs (Bayn Dzak or Bayanzag) of the Djadochta Formation, Gobi Desert, on 11 August 1923, Peter Kaisen discovered the first Velociraptor fossil known to science—a crushed but complete skull, associated with one of the raptorial second toe claws (AMNH 6515). In 1924, museum president Henry Fairfield Osborn designated the skull and claw (which he assumed to come from the hand) as the type specimen of his new genus, Velociraptor.
------
Stegosaurus, one of the many dinosaurs described in the Bone Wars, was first collected by Arthur Lakes - found by Marsh
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stegosaurus
------
Pterodactyl
The first Pterodactylus specimen was described by the Italian scientist Cosimo Alessandro Collini in 1784, based on a fossil skeleton that had been unearthed from the Solnhofen limestone of Bavaria. Collini was the curator of the Naturalienkabinett, or nature cabinet of curiosities (a precursor to the modern concept of the natural history museum), in the palace of Charles Theodore, Elector of Bavaria at Mannheim.[6][7] T
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pterodactylus
----'
Spinosaurus
1912, Richard Markgraf discovered a partial skeleton of a giant theropod dinosaur in the Bahariya Formation of western Egypt.
**** however, it
was destroyed in World War II, specifically "during the night of 24/25 April 1944 in a British bombing raid of Munich" that severely damaged the building housing the Paläontologisches Museum München (Bavarian State Collection of Paleontology). However, detailed drawings and descriptions of the specimen remain. Stromer's son donated Stromer's archives to the Paläontologische Staatssammlung München in 1995, and Smith and colleagues analyzed two photographs of the Spinosaurus holotype specimen BSP 1912 VIII 19 discovered in the archives in 2000.
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spinosaurus
__
Parasaurolophus
is based on ROM 768, a skull and partial skeleton missing most of the tail and the back legs below the knees, which was found by a field party from the University of Toronto in 1920 near Sand Creek along the Red Deer River in Alberta.[5] These rocks are now known as the Campanian age Late Cretaceous Dinosaur Park Formation. William Parks named the specimen P. walkeri in honor of Sir Byron Edmund Walker, the chairman of the Board of Trustees of the Royal Ontario Museum.[5
Parasaurolophus - Wikipedia
------
Diplodocus
The first record of Diplodocus comes from Marshall P. Felch’s quarry at Garden Park near Cañon City, Colorado, when several fossils were collected by Benjamin Mudge and Samuel Wendell Williston in 1877. The first specimen (YPM VP 1920) was very incomplete, consisting only of two complete caudal vertebrae, a chevron, and several other fragmentary caudal vertebrae. The specimen was sent to the Yale Peabody Museum and was named Diplodocus longus ('long double-beam') by paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh in 1878.
____
Brachiosaurus
Discovered by American paleontologist Elmer S. Riggs and his crew from the Field Columbian Museum (now the Field Museum of Natural History)
Brachiosaurus - Wikipedia
__<_
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carnotaurus
unearthed in 1984 by an expedition led by Argentinian paleontologist José Bonaparte - sponsored by the National Geographic Society
_____
Pachycephalosaurus
As determined by Donald Baird, in 1859 or 1860, Ferdinand Vandeveer Hayden, an early fossil collector in the American West, collected a bone fragment in the vicinity of the head of the Missouri River,
This specimen, ANSP 8568, was described by Joseph Leidy in 1872 as belonging to the dermal armor of a reptile or an armadillo-like animal.[7] It became known as Tylosteus. Its actual nature was not revealed until Baird studied it again over a century later and identified it as a squamosal (bone from the back of the skull) of Pachycephalosaurus, including a set of bony knobs corresponding to those found on other specimens of Pachycephalosaurus.
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pachycephalosaurus
_<<<_
https://www.levins.com/mount.shtml
Had to make replic cuz thugs
__<<
Dilophosaurus’s
1942, the paleontologist Charles L. Camp led a field party from the University of California Museum of Paleontology (UCMP) in search of fossil vertebrates in Navajo County in northern Arizona
-----
Other discoveries
a paper published last week in Royal Society Open Science, Poropat and his colleagues detail the similarities between Ann and another sauropod discovered in Argentina and described in 2016
https://www.smithsonianmag.com/smart-news/rare-95-million-year-old-dinosaur-skull-uncovered-in-australia-180982006/
Towering dinosaur with radioactive skull identified in Utah
Towering dinosaur with radioactive skull identified in Utah
Towering dinosaur with radioactive skull identified in Utah
World’s first 100% complete T-rex skeleton found locked in battle with a Triceratops
Entombed in sediment in Montana, they were discovered by professional fossil hunters – a cattle rancher cowboy and two pals.
https://www.theguardian.com/science/2023/apr/12/95-million-year-old-dinosaur-skull-discovered-in-queensland-belonged-to-rare-sauropod -
Archeologists say they began finding ‘limb bones and vertebrae’ but only realised they had found fragments of a skull when a brain case was identified. Photograph: Australian Age of Dinosaurs Museum of Natural History
_____
https://www.nytimes.com/2023/12/11/science/pliosaur-dinosaur-skull-dorset-uk.html
A North Carolina State University paleontologist finds his dream fossil in the sands of the New Mexico desert.
Found: Perfectly Preserved Dinosaur Skull
https://www.discovery.com/exploration/intact-parasaurolophus-skull-discovered-in-new-mexico-desert
T Rex skull
One Of The Most Complete T. Rex Skulls Ever Discovered Could Fetch $20 Million At Auction
The skull was excavated from private land that makes up a section of the Hell Creek Formation in South Carolina, which has yielded more tyrannosaur fossils than anywhere else on Earth, according to Sotheby’s.
https://www.cnn.com/2020/03/11/world/dinosaur-bird-head-skull-amber-scn/index.html
Beyond our imagination
The first dinosaur skeleton to be found entombed in amber was detailed in 2016 by Chinese paleontologist Lida Xing, who found the remarkable specimen of a dinosaur tail at an amber market in northern Myanmar.
https://www.inverse.com/article/20059-tyrannosaurus-rex-skull-discovered-hell-creek
Largest t rex
"discovered by a team of paleontologists and volunteers in northern Montana."
https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-56590733
Scientists in southern Argentina have found the skull of a large meat-eating dinosaur named "one who causes fear" in the local Mapuche language
https://abcnews.go.com/US/man-discovered-rare-70-million-year-dinosaur-skeleton/story?id=107776667.
Scientists Argentina
Skull of 'armless' meat-eating dinosaur discovered
Skull of 'armless' meat-eating dinosaur discovered
It likely used its head and jaws to take down prey.
Look into 2022, Damien Boschetto stumbled upon a massive, 70 million-year-old fossil that turned out to be a nearly complete skeleton of a long-necked titanosaur, he told ABC News.
****
While walking the dog, a landslide on the edge of the cliff exposed the bones of various skeletons," Boschetto said, according to the outlet, adding: "They were fallen bones, therefore isolated. We realized after a few days of excavations that they were connected bones."
https://www.businessinsider.in/science/news/a-man-stumbled-upon-a-70-million-year-old-dinosaur-fossil-but-kept-it-secret-for-2-years/articleshow/108188512.cms
Dinosaur skull turns paleontology assumptions on their head
Dinosaur skull turns paleontology assumptions on their head
Newly Discovered Tyrannosaur Was Key to the Rise of Giant Meat-Eaters
Newly Discovered Tyrannosaur Was Key to the Rise of Giant Meat-Eaters
A partial skull found in Alberta helps put a timer on when the 'tyrant lizards' got big
Other
Which Dinosaur Bones Are “Real”? - Field Museum
Which Dinosaur Bones Are “Real”? - Field Museum
Page scrubbed from Museum site Face to face with a perfectly preserved dinosaur that looks like it was alive yesterday
Face to face with a perfectly preserved dinosaur that looks like it was alive yesterday
An accidental discovery of a 3D fossil reveals the dinosaur’s mysterious death
Replicas Dinosaurs Skulls Fossil Replicas | Dinosaur Corporation
Dinosaurs Skulls Fossil Replicas | Dinosaur Corporation
Business closed - screebshot on phone
Dinosaur skull discovered in northeastern B.C. a first in the province
Dinosaur skull discovered in northeastern B.C. a first in the province
https://nypost.com/2022/08/26/82-foot-long-dinosaur-skeleton-found-in-mans-backyard-in-portugal/
https://www.smithsonianmag.com/science-nature/the-top-ten-dinosaur-discoveries-of-2023-180983403/
When was the first recorded dinosaur found in Alberta? A: On August 12, 1884, Joseph B. Tyrrell stumbled upon a 70-million-year-old dinosaur skull, the first of its species ever found, just a few kilometres from where the Royal Tyrrell Museum now stands.
https://www.multivu.com/players/English/7540751-travel-alberta-dinosaur/links/7540751-Dino-Fact-Sheet.pdf
https://www.rfi.fr/en/science-and-technology/20200806-77-million-year-old-fossil-in-canada-reveals-dinosaurs-got-cancer-science-research
https://thedinosaurs.org/dinosaurs/centrosaurus
Mummified “Nadosaurus” was magically discovered only a few years prior, in 2011.
shortly.
https://collections.peabody.yale.edu/search/Record/YPM-VPPU-012749
Subscribe to Agent131711’s Substack
I'm a researcher. Come explore uncomfortable Truths in a lighthearted way that makes them easier to digest (and sometimes even hilarious). I publish special deep dives for paid subs on the 1st and 15th, everything else is free.
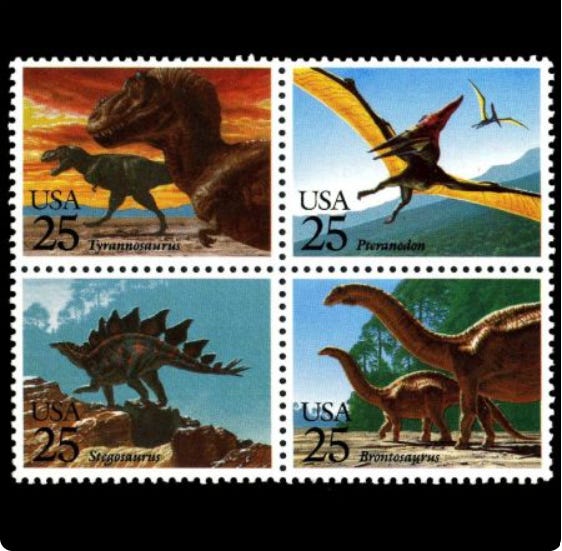
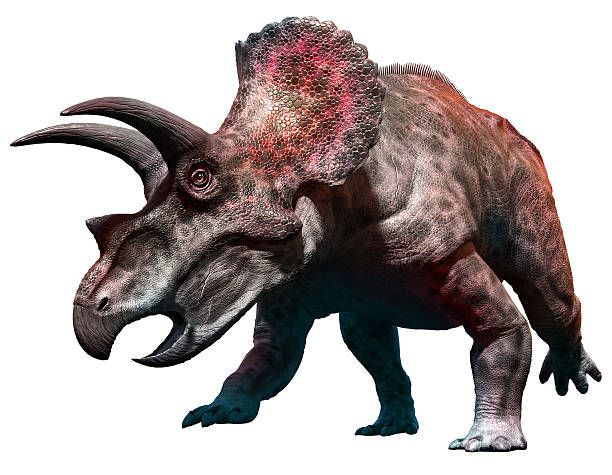
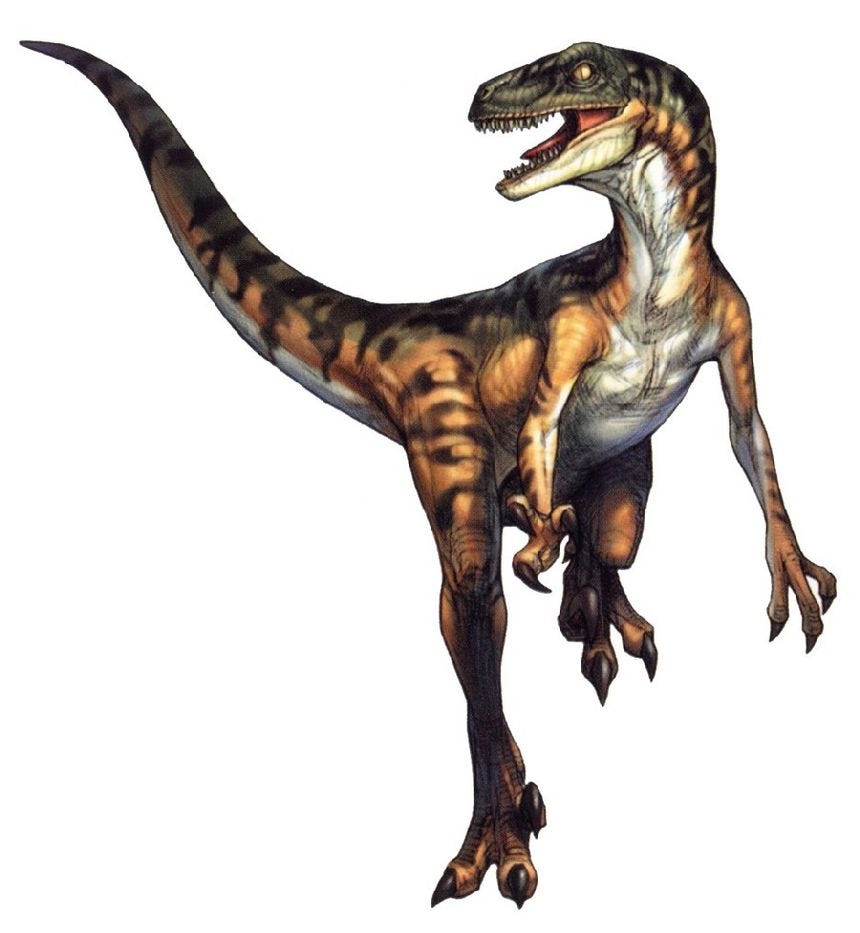
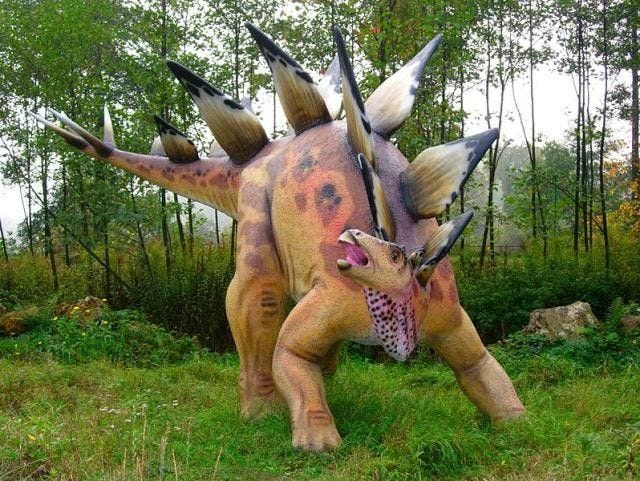
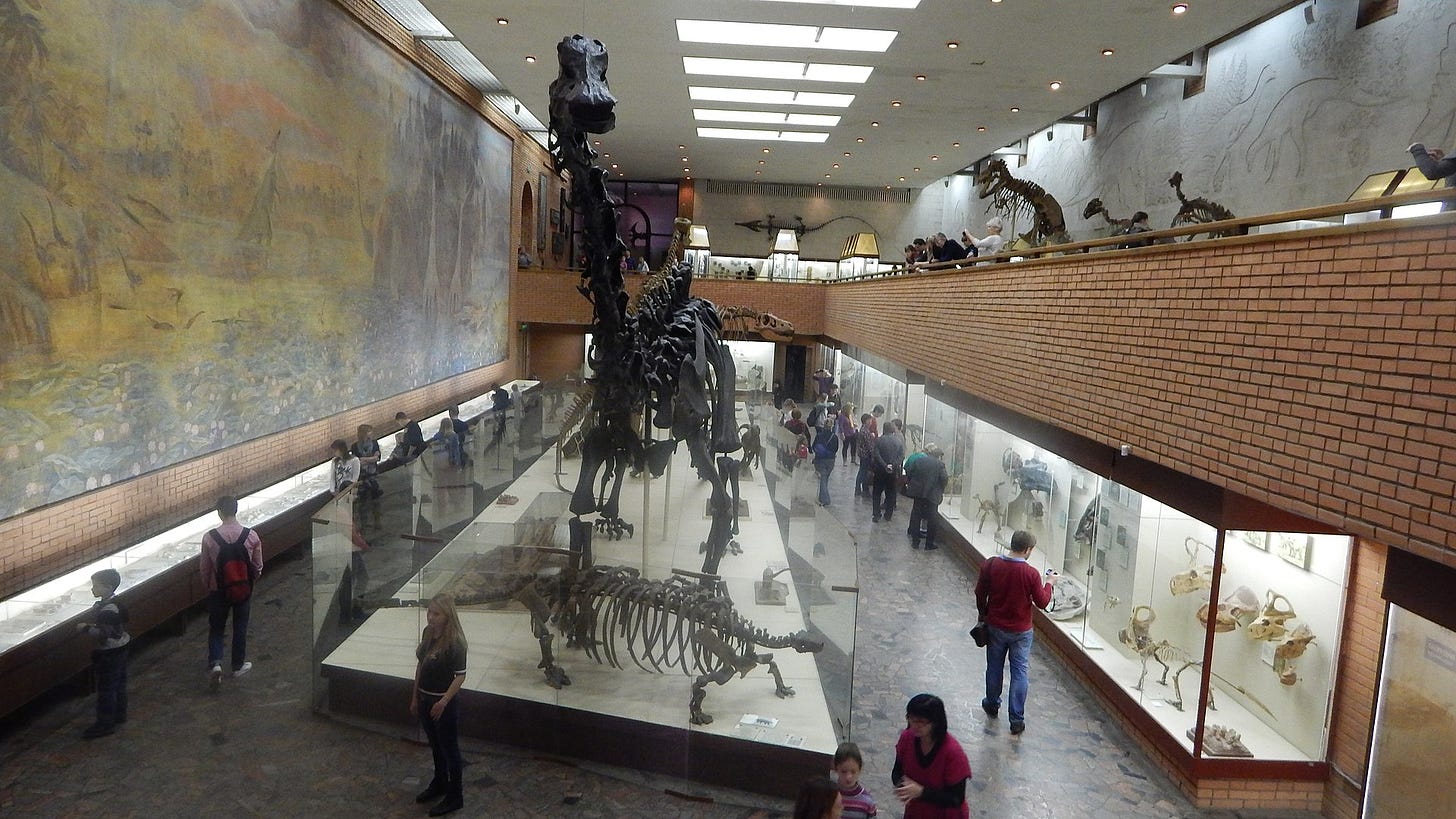
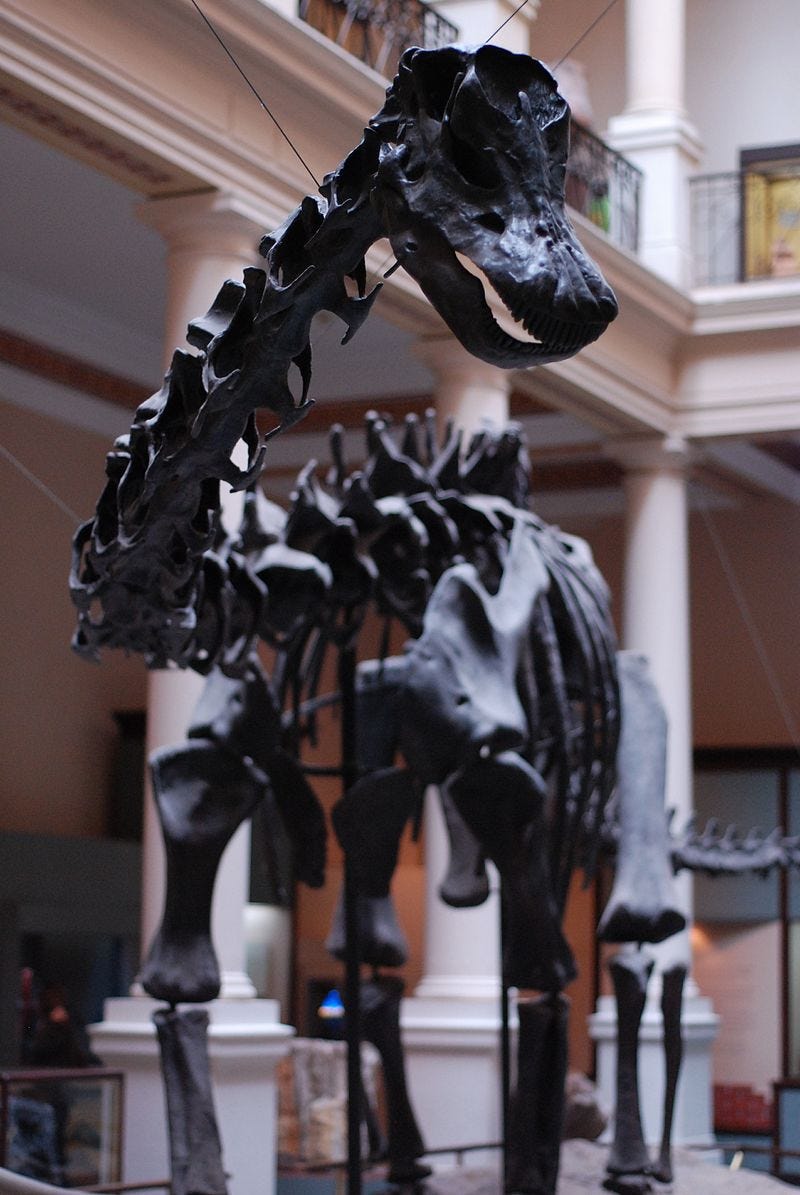
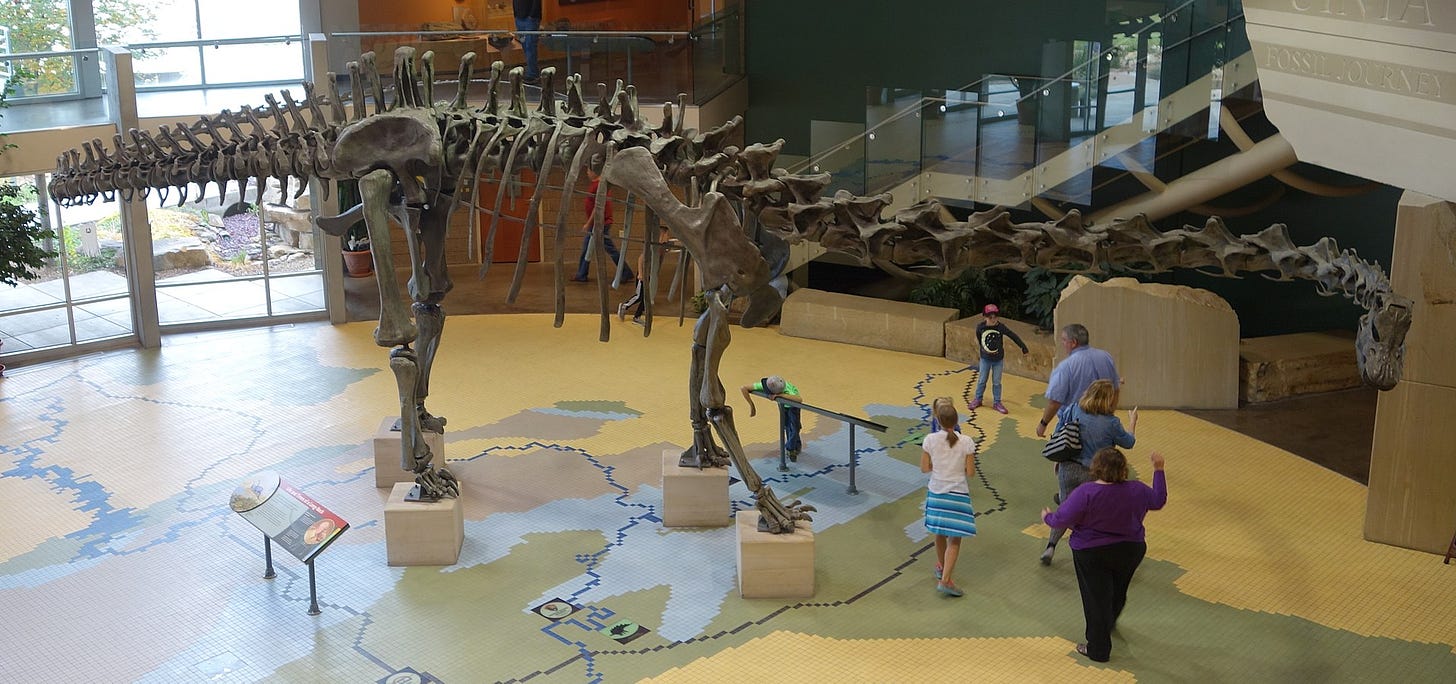
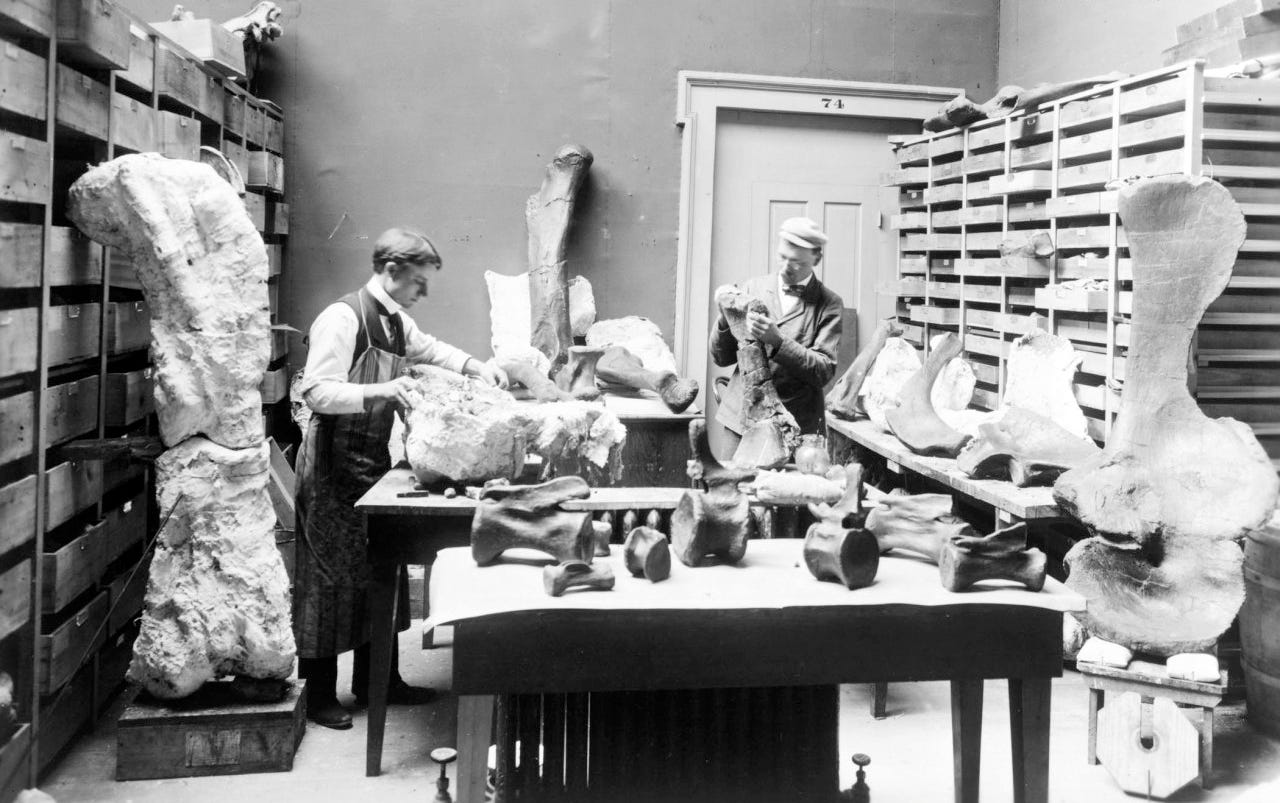
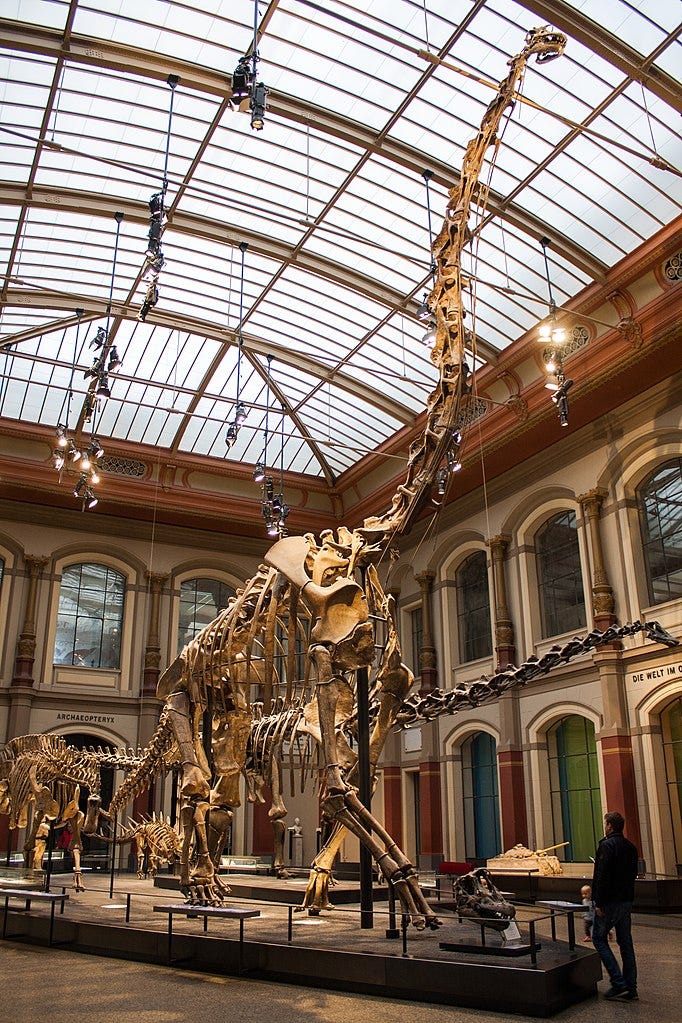
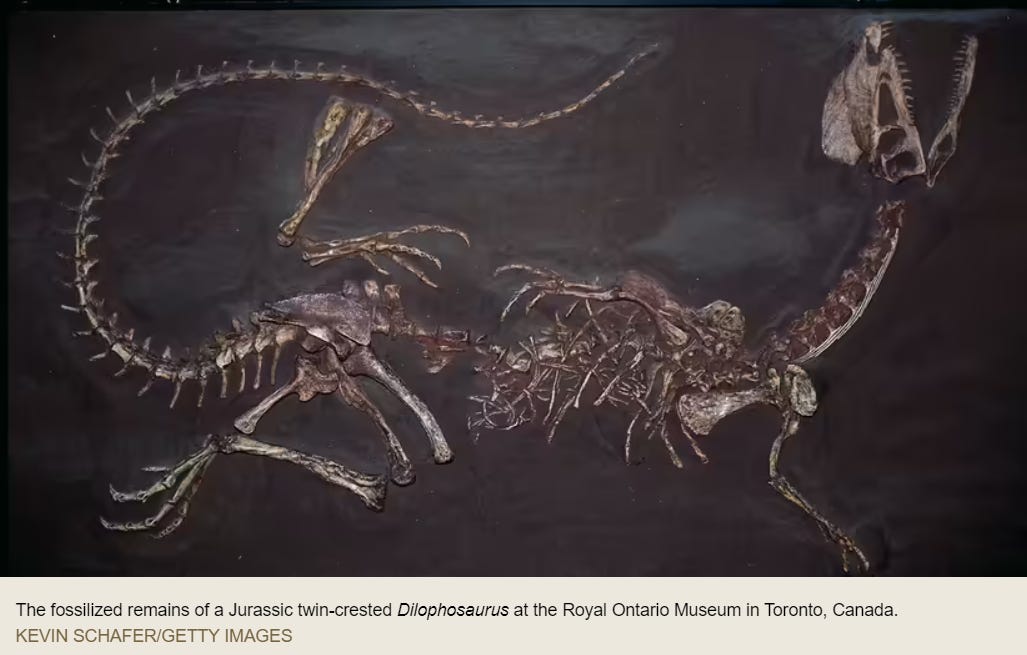





























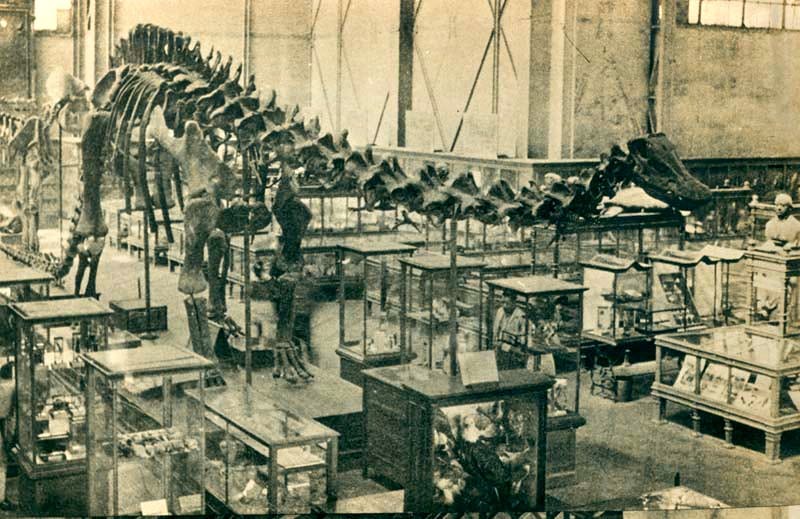


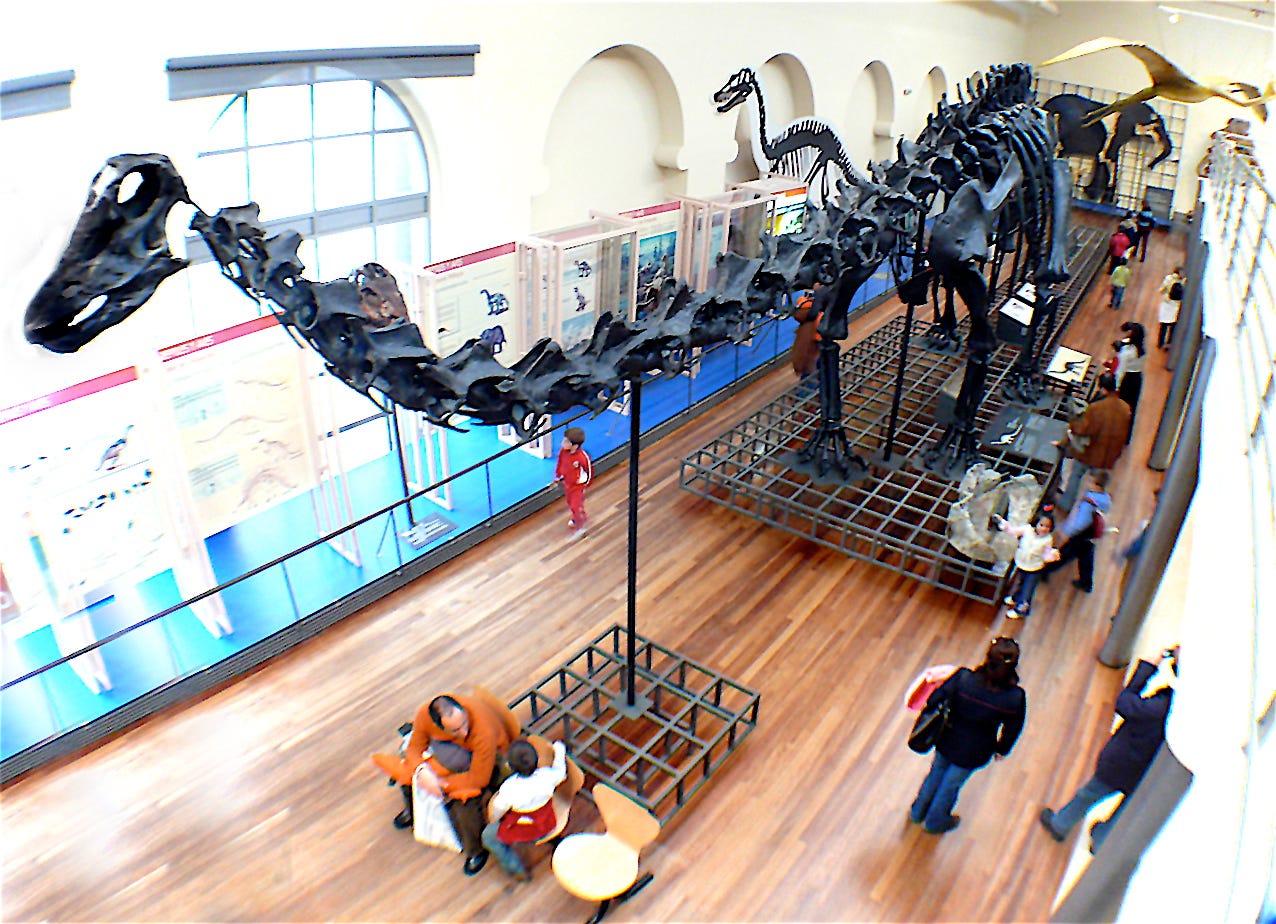


































If the long con is to replace the idea of a 'creator' with the randomness of 'evolution', it seems like a lot of time and money invested for not much in the way of results with the ongoing Jurassic Park charade.
Does the belief in the pre-existence of giant lizard creatures automatically null and void everyone's idea of "God"? I mean, do people spend a lot of time thinking about dinosaurs? "Oh, look at these pictures of giant lizards...there must be no God....let's all just be nihilists and have big bang parties." People still gonna believe...
There has to be more to this as a cover story. But I reckon 'evolution' as a backdrop has entanglements with our friends in modern medicine who like to tell stories about DNA and genes as well...
Is it merely coincidence that Brown and P.T. share the name "Barnum"?
I am not a paleontologist, and I did not stay at a Motel 6 last night, but it appears to me that they share a bit more than just a name.